Search engines, like Google, make finding information online quick and simple, particularly when we are performing broad searches like online shopping, finding a new restaurant, or looking for a job. However, when searching for information about individuals, persons of interest, businesses, or other more specific targets, the number of results returned from Google can be overwhelming. Luckily, Google has incorporated methods of narrowing results into their search engine. These are commonly known as Google dorks (or Google hacking). Today, we are going to go over some of the most common and useful Google dorks for open source intelligence (OSINT) investigations.
How Do Google Dorks Work? 🔗︎
Most of us begin our online searching by merely typing keywords into the search bar, but in doing so, we have already missed an opportunity to optimize our results. Google dorking makes use of commands called Operators that allow users to modify their search results in many ways. For instance, a user searching for information related to private universities in the United States could type Harvard AND Stanford into Google to only return search results that contain both keywords. Note that Google dorks are case-sensitive, so typing Harvard and Stanford would not generate the same results. While this is a very simple Google dorking technique, there are many more that allow users to modify search results in more profound ways.
Many of these techniques are useful on their own. Still, much of their utility is derived from the user’s ability to combine them to return very specific results from Google.
By using these Operators in combination with each other (and the many others that exist), users can target specific information more easily.
Let’s look at two of these Operators quickly to see how they work together to return specific results.
The site: Operator allows us to perform a Google search that will only return results that are hosted on the designated site. For instance, Harvard site: Wikipedia.org will only return search results related to the keyword Harvard from Wikipedia.org.
The – (minus) Operator allows the user to exclude specific results from their search. By combining these two Operators, we can create the search Harvard -site: Wikipedia.org, which will return search results from Google while excluding any results from Wikipedia. As you become more proficient with each Operator, you will also find more ways to combine these Operators to find useful information regarding your investigations.
To utilize the power of combining Google search Operators, though, we need to learn a few more. In this PDF cheat sheet, we list out all the useful Google dorks (search operators). Download the cheat sheet now to start using them!
Who Can Use Google Dorking? 🔗︎
While anyone can benefit from using Google dorks, the focus of this article is to highlight the usefulness of these techniques for those conducting open source intelligence investigations, particularly regarding person-of-interest (POI) investigations. Investigators have been turning to the internet, search engines, and social media for years to find information that might prove helpful, but Google dorking techniques can take your OSINT information gathering to a new level!
Let’s look at a couple of unique examples that might be useful in your next investigation.
Useful Google Dorks for Person Investigations 🔗︎
1. Finding Email Addresses Related to a Username 🔗︎
If you are like most people, you probably have one username that you use for many different accounts across the digital landscape. This username sometimes contains bits of personal information, like a person’s name, year of birth, or favorite sports team, but the real value in terms of an investigation is finding out whether that username has been used elsewhere online. While someone may take precautions to be private or secure with an account that is tied to criminal or mischievous behavior, other of their accounts may not be as well guarded.
Let’s say that you are looking into a person-of-interest and the only information you have about this individual is a username: BadGuy1. While a search for BadGuy1 might return other places that the username shows up online, by using the Wildcard Operator and searching for BadGuy1*com, we can instead see if any email addresses appear publicly online that use the username as the unique identifier.
While this will not always return significantly different results to searching the username itself, it can be used as a quick way to identify an email address that can later be tied to other accounts.
2. Uncovering New Contact Information from Online Documents 🔗︎
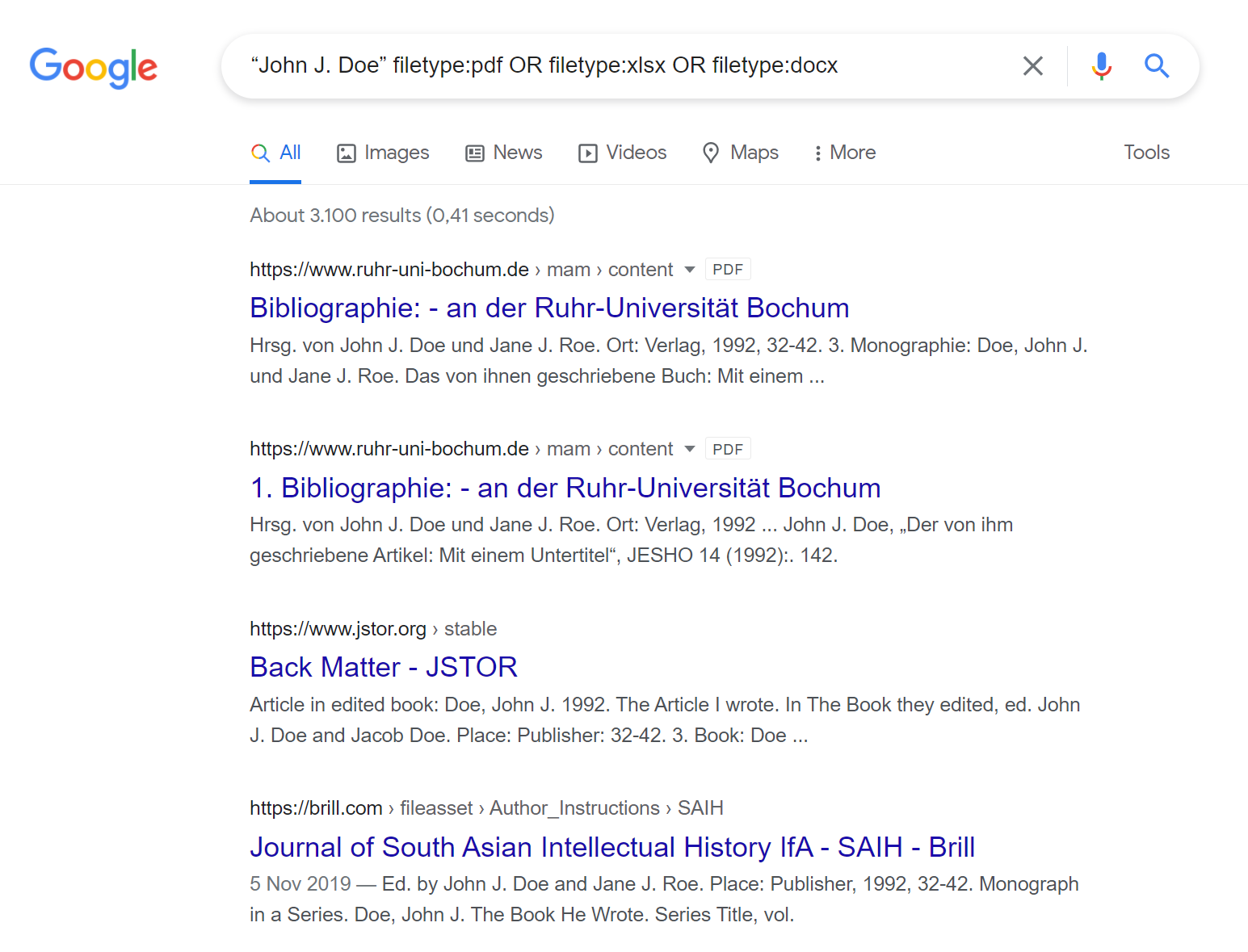
Perhaps you have a subject’s name, but you have little else to go on to learn more. There is a lot that we can learn about an individual given only their name, but our subject, John J. Doe, has a small digital footprint on typical social networking sites or apps. Instead, let’s see what we can find out about our subject using documents that are hosted online.
In the search bar we can enter “John J. Doe” filetype:pdf OR filetype:xlsx OR filetype:docx which will give us only PDF, Excel, or Microsoft Word documents containing the exact search term John J. Doe.
Here we have combined three different search Operators to improve our results, which can save a lot of time and effort over the course of an investigation. For John J. Doe, most of the documents that were returned used the fictitious name to make examples or protect identities. However, when using a real person’s name, the documents found might include court records, resumes, or other official documents that can give insight into a person’s life, finances, family, or friends.
3. Gaining Information Through Social Media 🔗︎
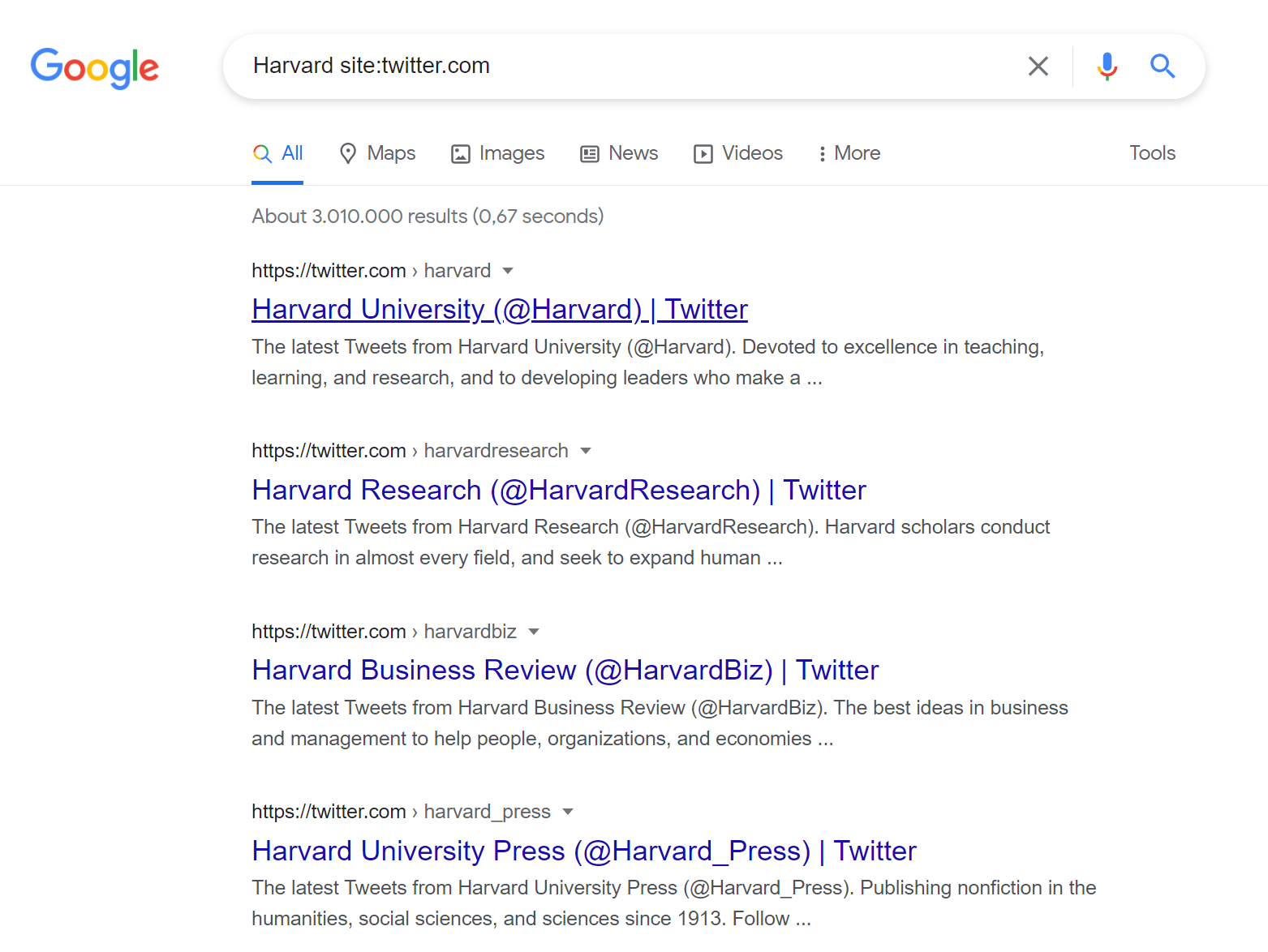
Even though John J. Doe doesn’t have much of a social media presence, that doesn’t mean that other persons-of-interest won’t. Social media platforms offer a wealth of information related to people, places, businesses, and networks. This information is often publicly available and poorly secured, so it makes for a wonderful place to search for knowledge to benefit an investigation. To search social media platforms, we can use the site: Operator again.
This time, we will search Harvard site:twitter.com to return only results on Twitter. The initial results that we receive are primarily dedicated different Twitter accounts related to Harvard University. However, diving deeper into the search results shows specific tweets, videos, and more.
Another interesting application is to search multiple social media platforms at the same time using our OR Operator. This can help us find accounts that are linked to the same individual across multiple platforms.
In addition, let’s say that our subject sent a tweet, but we want to see if that exact language appears anywhere else online. We could search “subject tweet content” – site:twitter.com in order to see if that exact phrase is used on another platform or by another account. This can help unmask networks of individuals working together, multiple accounts run by one individual, or accounts across different platforms that may have varying levels of security.
Google dorks are useful tools that can significantly improve investigations for cybersecurity and cybercrime investigators. There are many other resources out there that dive deeper into the uses of Google dorks, but we hope that this introduction has piqued your interest! If you want to learn more about dorking techniques for the Bing search engine, check out our blog post here.
Download the Full List of Useful Google Search Operators 🔗︎
Download our Google Dorks cheat sheet now to see the full list of useful Google search Operators. Print it out and share it with your colleagues and teams!
Follow Maltego on Twitter and LinkedIn for more tips and tricks, and subscribe to our email newsletters to learn more about how we can help with your next investigation!