Maltego has been instrumental in supporting various types of fraud investigations through a wide range of data integrations into our Transform Hub. With Maltego, fraud investigators can deepen and further contextualize their analysis with specific data sources by combining millions of attribution data points from OSINT or third-party intelligence providers.
As part of our Transform Hub, CipherTrace Transforms provide investigators, analysts and researchers with access to a wealth of cryptocurrency intelligence from the different digital tokens, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, Bitcoin Cash and Litecoin. Leveraging open and closed source blockchain attribution and machine learning algorithms, CipherTrace Blockchain Intelligence assists law enforcement investigators and financial fraud specialists to de-anonymize transactions and obtain solid evidence on individuals involved in money laundering, financial terrorism, drug dealing, extortion and other crimes.
Money Laundering with Cryptocurrency 🔗︎
With CipherTrace Transforms, users can trace tainted Bitcoin addresses and transactions and identify risky transaction characteristics and locations, including known criminal, dark market, gambling sites, and mixing services.
Mixing services, also known as Mixers, Tumblers, or Foggers, are services that offer users the opportunity to mix potentially identifiable or “tainted” cryptocurrency funds with others, making it difficult to follow the trail back to the original source of the fund. While mixing helps legitimate cryptocurrency users protect their privacy, it can also be abused by criminals for money laundering purposes by mixing illegally obtained funds with legitimate ones. Mixing large amounts of money may also be illegal or in violation of anti-money laundering laws.
This is where Maltego’s CipherTrace data integration comes into play, allowing the investigation and further contextualization of suspicious use of cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin Forensics with Maltego and CipherTrace 🔗︎
Essentially, the Maltego and CipherTrace integration connects the dots between disparate elements of the digital evidence involved in money laundering as well as criminal or illicit use of cryptocurrencies. It also enables cryptocurrency investigations to be tightly coupled and interrelated with different pieces of the digital puzzle.
In this tutorial, we will introduce the CipherTrace Transforms and show how Bitcoin forensics or cryptocurrency investigations can be carried out in Maltego.
Download and watch our CipherTrace webinar, where we demonstrate how law enforcement agencies and cryptocurrency analysts alike can trace Bitcoin and Ethereum movements, gather evidence of fraud, and identify the malicious actors behind a complex transaction.
To start, download the Maltego Desktop Client, then inquire for a trial access to the API key of CipherTrace here. Once a trial API key has been granted, head to the Transform Hub in the Maltego Desktop Client to find and install the CipherTrace Hub item which includes 13 Transforms.
CipherTrace Cryptocurrency Transforms Overview 🔗︎
The CipherTrace Cryptocurrency Transforms operate at three levels: Bitcoin Address, Bitcoin Transaction and Bitcoin Wallets.
In short, the Bitcoin Address and Bitcoin Transaction Transforms enable users to calculate the current state of a coin or transaction, such as its risks and attribution details. Bitcoin Wallet Transforms help users to aggregate multiple Bitcoin addresses into clusters that may point to a single owner or service.
In this tutorial, we will cover the functions of all three levels of CipherTrace Cryptocurrency Transforms with a simple demonstration.
- CipherTrace Bitcoin Address Transforms: Investigating Inbound & Outbound Transactions
- CipherTrace Bitcoint Transaction Transforms: Mapping Money Laundering Footprint
- CipherTrace Bitcoin Wallet Transforms: Identifying Wallet Owners & Locations
CipherTrace Bitcoin Address Transforms 🔗︎
A Bitcoin address is a public cryptographic key that “processes” or “locates” the Bitcoins. This address is used to uniquely identify Bitcoins and is typically stored on a users’ computer or mobile device app. Persons who know the corresponding public key can send Bitcoins to any other addresses.
Using the CipherTrace Bitcoin Address Transform, users can explore the Bitcoin address and enhance these results with additional details returned from fetching IP addresses, inbound and outbound transactions and wallet transaction data.
Investigating Inbound and Outbound Transactions 🔗︎
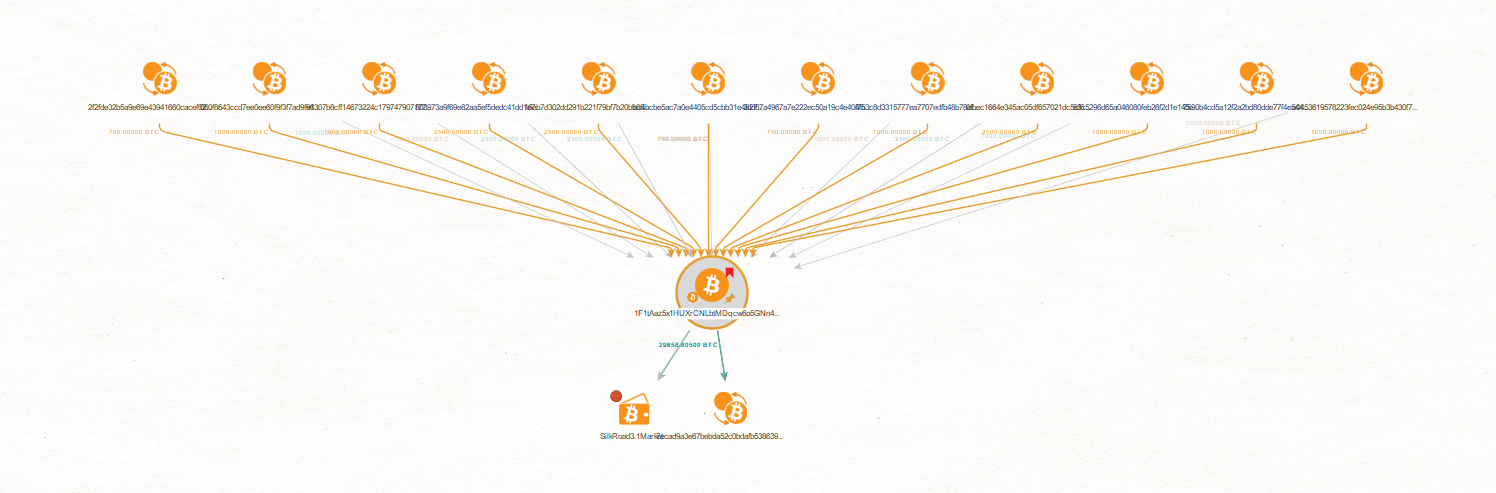
In this example, we will begin by dragging and dropping a Bitcoin Address Entity into Maltego to start our investigation. We will be using the pre-input address attribution given by the CipherTrace Entity.
We run the “To Detail [CipherTrace]” Transform and obtain a variety of useful information that showcase a money laundering activity.
As shown in the below graph, there are multiple inbound Bitcoin Transaction Entities associated with this Bitcoin Address Entity. The Bitcoin address is also connected to an Outbound Transaction Entity as well as to a Bitcoin Wallet Entity.
We can attempt to expand these results by running the “To Inbound Transaction [CipherTrace]” Transform and the “To Outbound Transaction [CipherTrace]” Transform. These Transforms allow users to identify the transaction history of the Bitcoin in the blockchain forensics data. This is helpful for tracing tainted addresses and evaluating the risks associated with the Bitcoin addresses, transactions and wallets.
The resulting graph, shown below, reveals additional inbound transactions going into the same Bitcoin address, but no additional outbound transactions.
Evaluating Risk Association of Bitcoin Addresses 🔗︎
What is unique and powerful about CipherTrace Cryptocurrency Intelligence is that it not only documents address and transaction records, but also marks any criminal or illicit history associated with a cryptocurrency.
Address risk scores are determined through deep research and automated analysis into address interactions and past transactions. When an address has no record of negative attribution or risky behavior, it is given low-risk scores. If the address is directly associated with, or involved in illegal or high-risk interactions, it is given high-risk scores.
Run CipherTrace Transforms to Retrieve Bitcoin Risk Evaluations 🔗︎
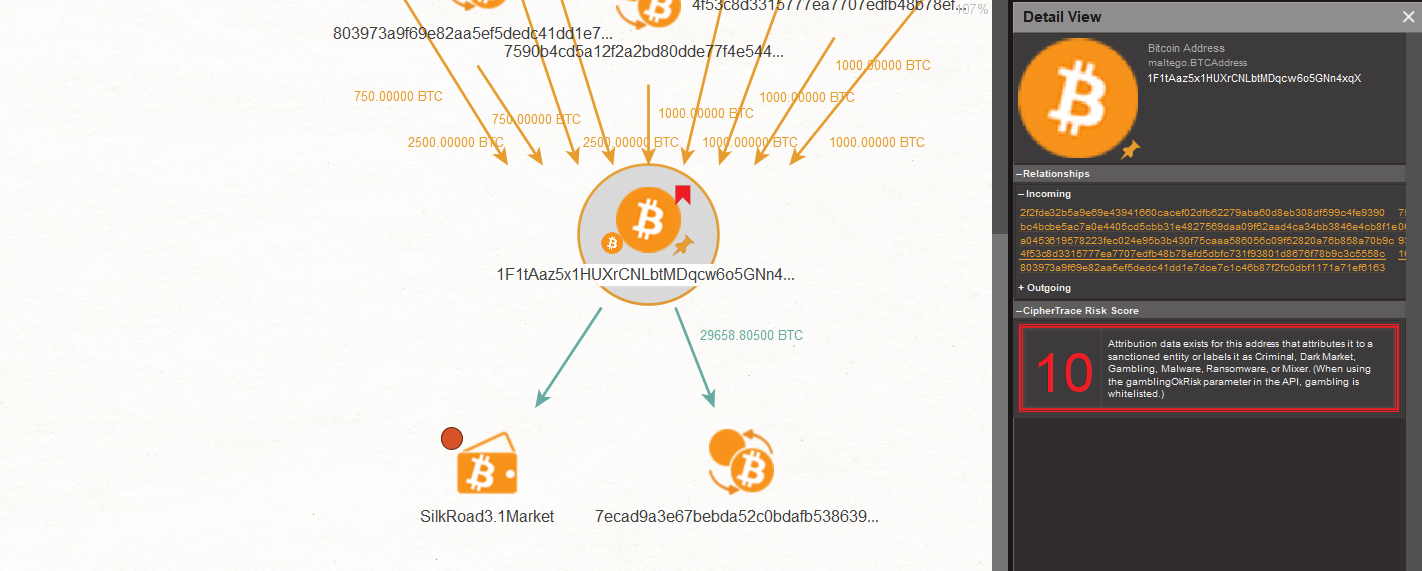
Users can either run the “To Address Risk Score [CipherTrace]” Transform on the Entity to return the risk score directly on the Maltego graph, or run any of the other CipherTrace Transforms and the risk score will be automatically displayed on the Detail View in the Maltego Desktop Client.
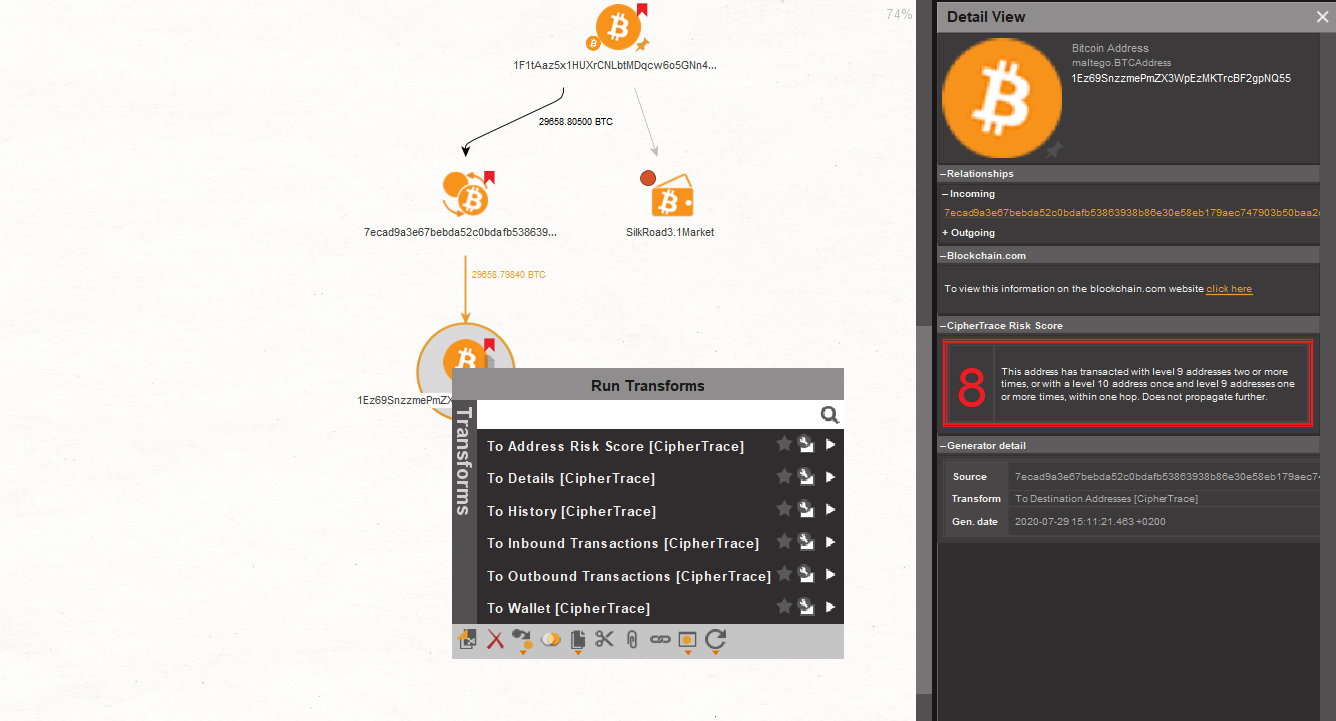
In our case, the risk score is automatically displayed on the Detail View after running the previous Transforms on our Bitcoin Address Entity. We can see that the Bitcoin address we used as a departure point is labeled as “High Risk” with a risk score of 10 in the CipherTrace Risk Score Section on the Detail View in the sidebar. CipherTrace also automatically bookmarks the Entity in red if it has a high-risk score.
By looking at the Detail View, we can see that it states that this Bitcoin Address Entity is attributed to a sanctioned Entity or has been labeled as Criminal, Dark Market, Gambling, Malware, Ransomware, or Mixer.
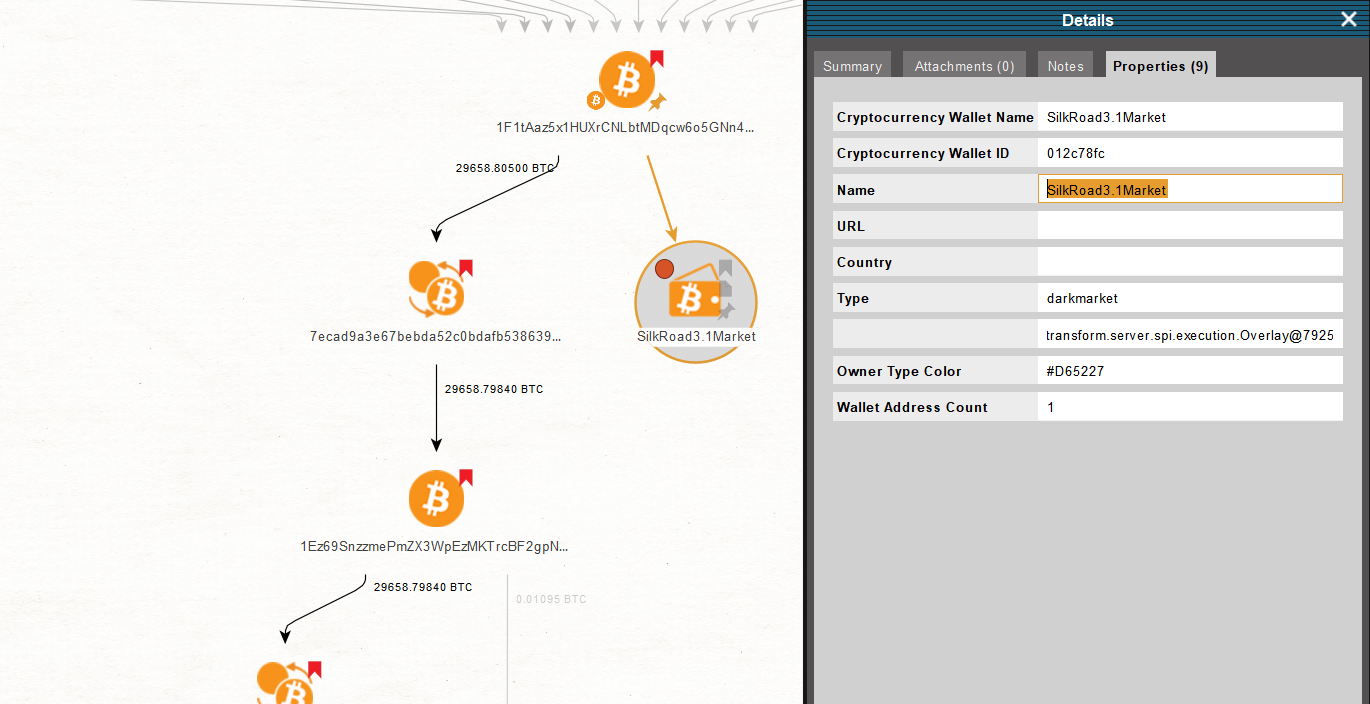
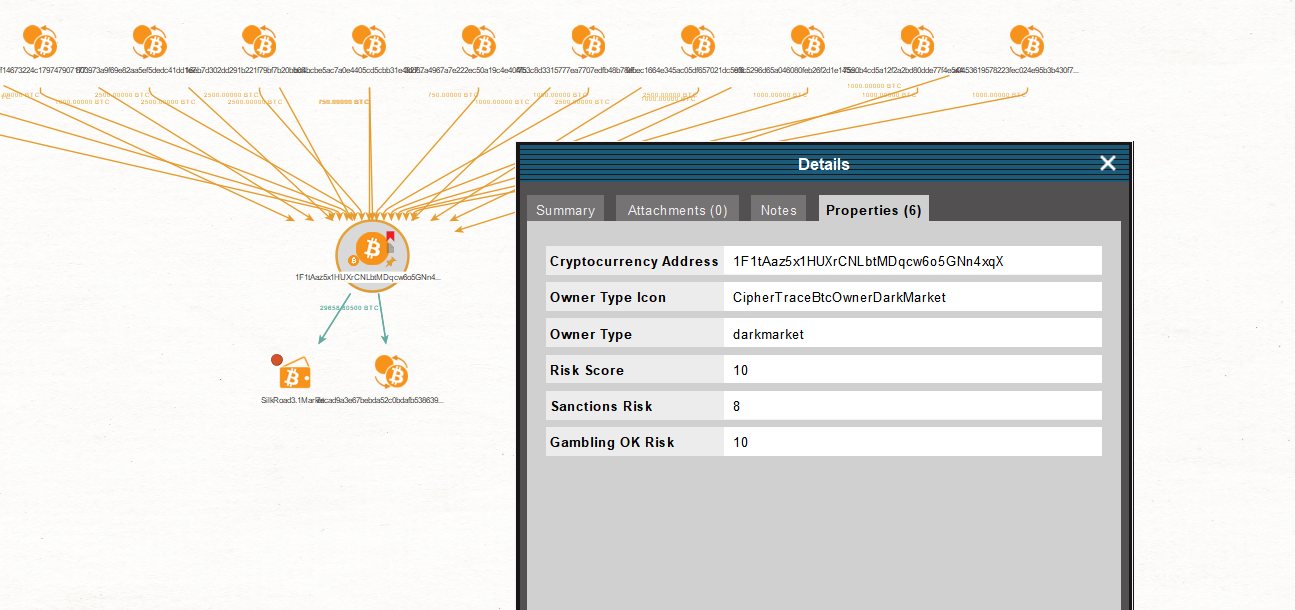
If we double click on the Entity and call out the Details Window, in the Properties tab, we can see that this Bitcoin address has a “darkmarket” Owner Type, among other details and risk scores.
Please note that if a transaction ID is input into the Bitcoin Address Entity instead of the Bitcoin address, the Transforms run will return no results.
CipherTrace Bitcoin Transaction Transforms 🔗︎
Besides conducting address-based investigations, users can also perform a trace based on transactions, using the Bitcoin Transaction Entity.
A transaction is a record in the public Bitcoin blockchain that records the movement of Bitcoins, or portions of them, from one address to another. Transactions are uniquely identified by transaction IDs. A transaction typically has one or more outputs that are shown in the CipherTrace Transaction Transforms list.
Uncovering Bitcoin Addresses Involved in Certain Transactions 🔗︎
The CipherTrace transaction tracing options include destination addresses, source addresses and risk scoring. Transaction risk scores are aggregated based on the input and output addresses. As with the Bitcoin Address Entity, the transaction risk score can be returned by running the “To Transaction Risk Score [CipherTrace]” or the other two CipherTrace Transforms shown in the image below.
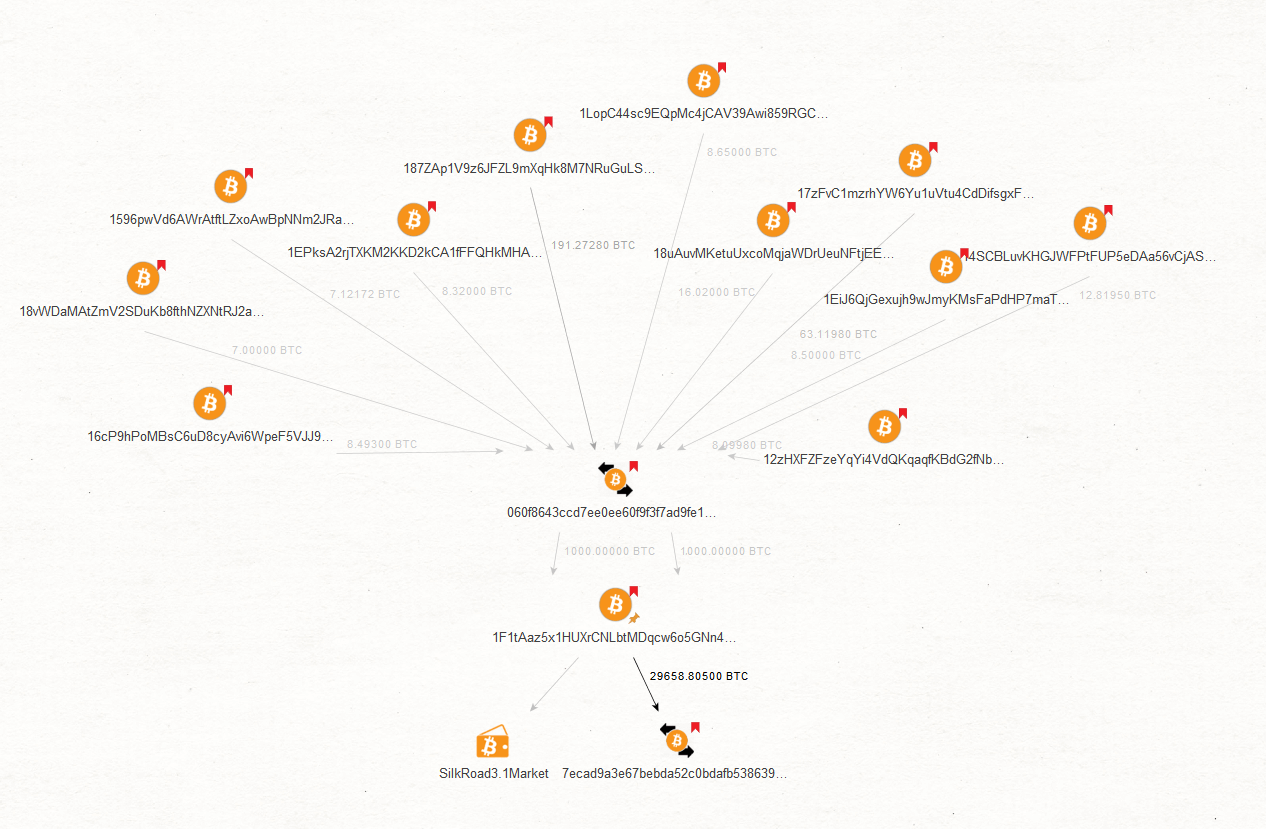
We pick one of the Inbound Transaction Entities, run the “To Source Addresses [CipherTrace]” Transform, and discover a number of high-risk Bitcoin addresses bookmarked red.
Cleaning up the graph, we can see clearly which Bitcoin addresses were related to the particular inbound transaction.
Returning to our initial results, we now know that the Bitcoin address we used as a departure point has a risk score of 10 and has been linked to criminal activities including money laundering.
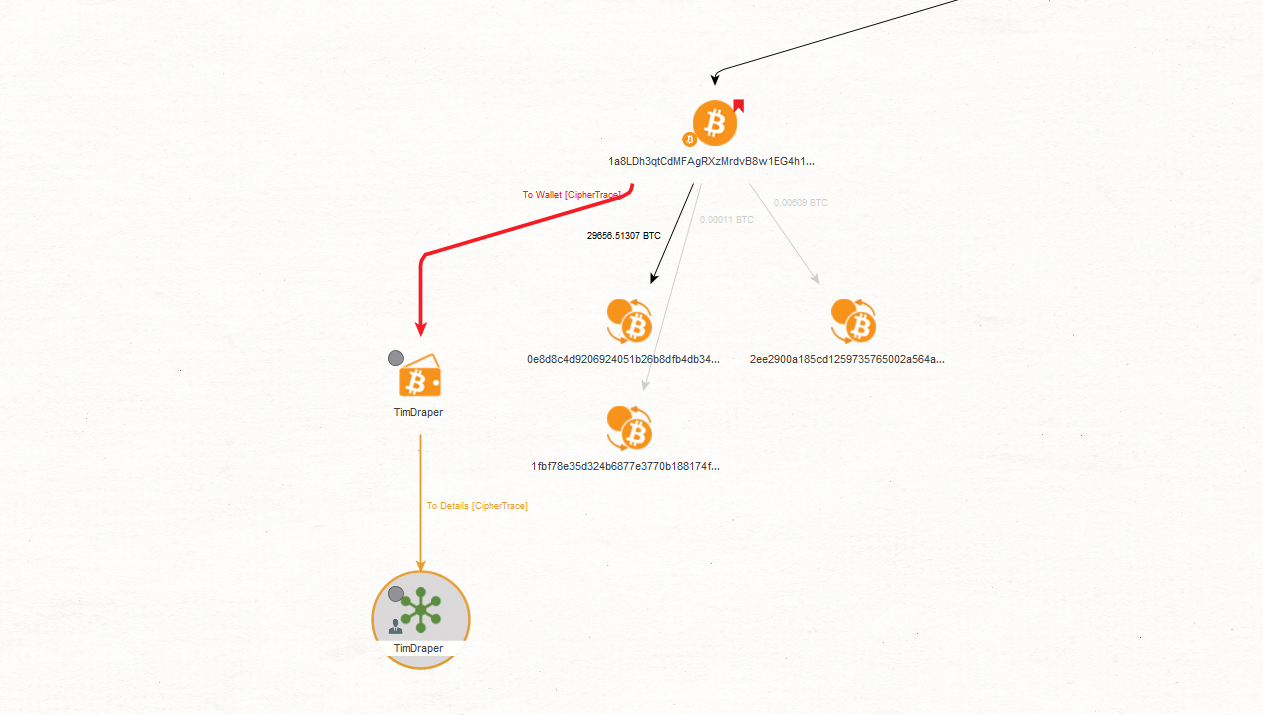
Next, we attempt to confirm our suspicions by taking a closer look at where the Bitcoins are going by running the “To Destination Address [CipherTrace]” Transform on the one outbound Bitcoin Transaction Entity connected to said address.
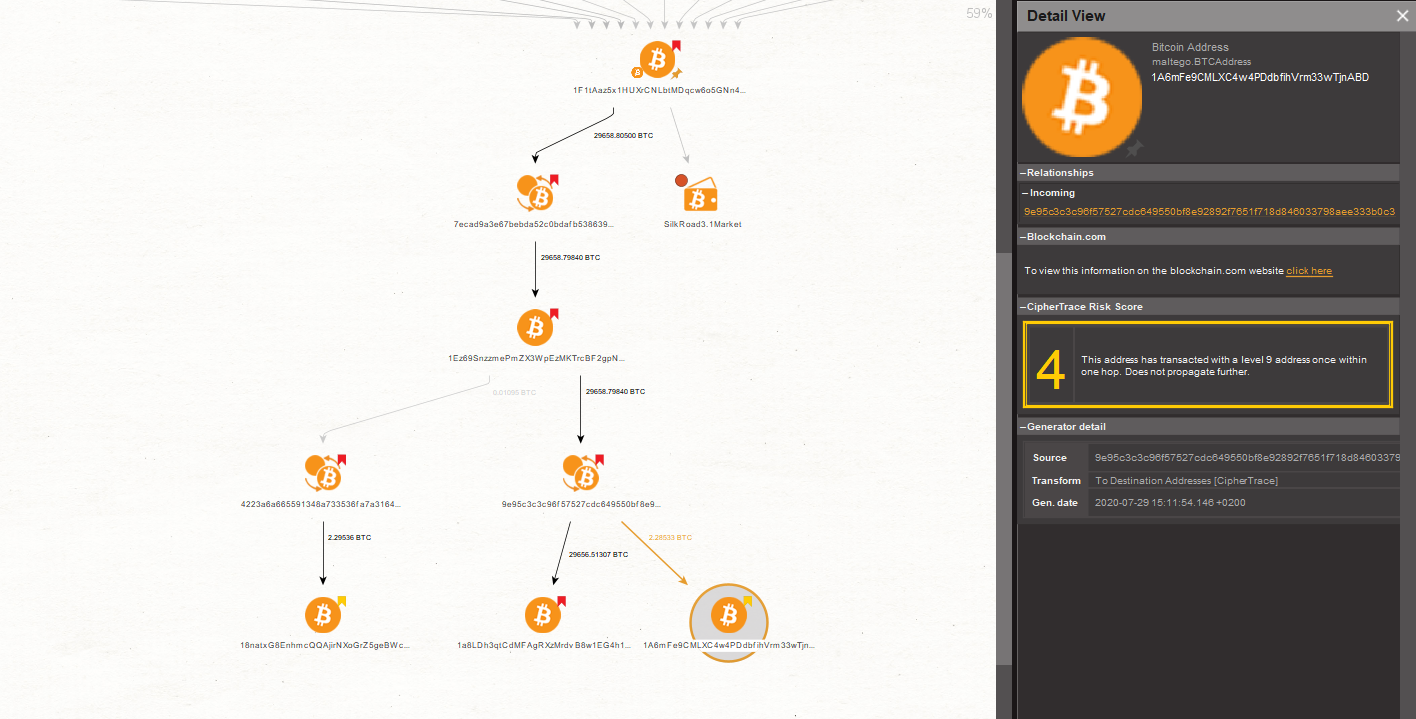
The Transform uncovers the Bitcoin address to which the transaction was made. Note that the risk score of this Entity has a lower risk score of 8. This could mean that this specific address has also received transactions which are less suspicious in comparison to the other address.
Next, we run the “To Outbound Transaction [CipherTrace]” on the Bitcoin Address Entity. After having discovered two more outbound transactions, we attempt to deepen the investigation and run the “To Destination Address [CipherTrace]” Transform again to reveal which addresses now possess the Bitcoins.
We can see that the two destination addresses returned by the Transforms we ran have a risk score of 4. This would confirm our hypothesis that through mixing activities, money launderers are able to gradually “wash away” the obvious association between the cryptocurrency and the criminal provenance of the funds behind it.
Please note that if a Bitcoin address is input into the Bitcoin Transaction Entity instead of the transaction ID, the Transforms will not return results.
CipherTrace Bitcoin Wallet Transforms 🔗︎
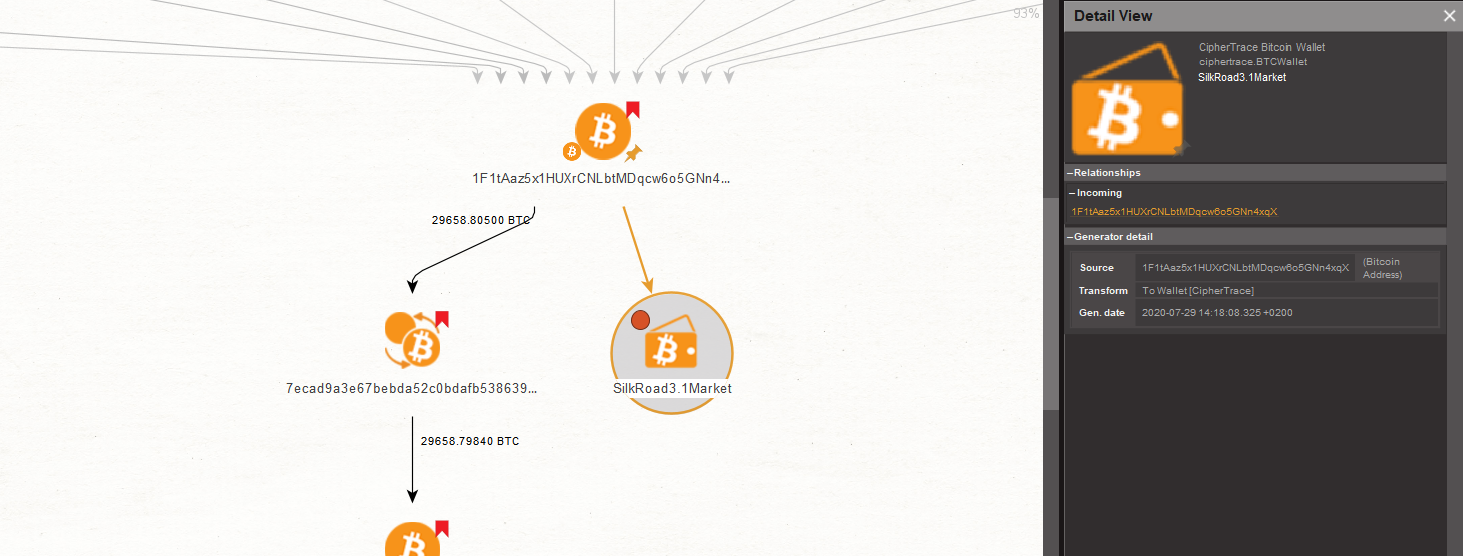
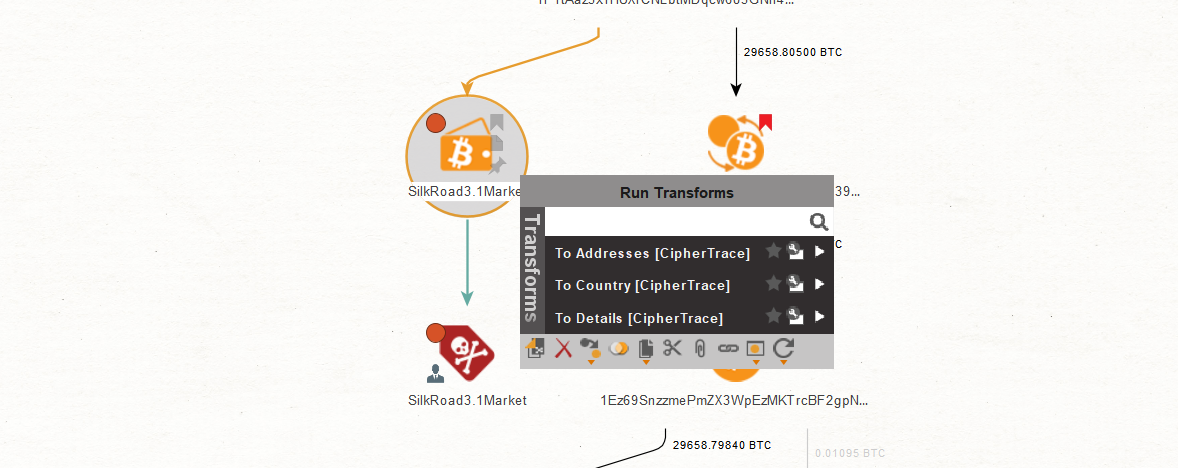
When we previously ran the “To Details [CipherTrace]” Transform on our first Bitcoin Address Entity, the Transform linked the Bitcoin address to a Bitcoin Wallet Entity.
CipherTrace uses multi-input clustering algorithms and machine learning to analyze multi-input transactions and connect them with known patterns. The relevant Bitcoin addresses are grouped into a “wallet” that is likely controlled by a single user or by a service, and which can be used to identify exchanges, locations and other information.
It is however important to note that the resulting identified wallet may not necessarily be 100% accurate nor representative of an individual.
The Bitcoin wallet we uncover is named “SilkRoad3.1Market.” According to the Properties in the Detail View Window, it is a type of dark web market.
Pivoting from Bitcoin Wallet Entity to Deepen Investigations 🔗︎
From a Bitcoin Wallet Entity, users can pivot to other related addresses, their geographic location and more information, for example, the cryptocurrency owner identified by CipherTrace. In this case, we were only able to link to the cryptocurrency owner “SilkRoad3.1Market.”
In some cases, when we pivot from a Bitcoin address to a Bitcoin wallet and run the “To Details [CipherTrace]” Transform, the Cryptocurrency Owner Entity returned could be assumed to be a name.
In order to drill deeper into this type of investigation, users can convert this Cryptocurrency Owner Entity into other Entity types such as an Alias to pivot and further investigate a person of interest using Maltego Standard Transforms, or with OSINT and third-party data sources provided by Maltego’s Data Partners.
Using CipherTrace to Map Out Cryptocurrency Fraud Activities 🔗︎
Especially useful for Law Enforcement Agencies, Financial Intelligence Units and Financial Institutions, the CipherTrace integration with Maltego can empower technical or non-technical agents, analysts, and fraud investigators to trace illicit cryptocurrency activities.
From pivoting on one suspicious Bitcoin address to mapping out the complete chain of transactions, addresses, and wallets, CipherTrace Cryptocurrency Intelligence enables users to quickly gain a comprehensive understanding of complex cryptocurrency exchanges. Through further investigation on the Bitcoin Wallet Entity, users can enrich and expand their investigations with other data sources to profile or track down targets.
Read more about CipherTrace data and Transforms here or request an API key here.
Don’t forget to download and watch our CipherTrace webinar, where we demonstrate how law enforcement agencies and cryptocurrency analysts alike can trace Bitcoin and Ethereum movements, gather evidence of fraud, and identify the malicious actors behind a complex transaction.
Follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn or subscribe to our email newsletter for new use cases, product updates and news!


![Run the “To Details [CipherTrace]” Transform](https://www.maltego.com/images/uploads/ciphertrace005.png)
![Run the “To Source Addresses [CipherTrace]” Transform on the Bitcoin Transaction Entity](https://www.maltego.com/images/uploads/ciphertrace009.png)
![Run “To Source Addresses [CipherTrace]"](https://www.maltego.com/images/uploads/ciphertrace010.png)
![Run “To Destination Address [CipherTrace]” Transform](https://www.maltego.com/images/uploads/ciphertrace011.png)